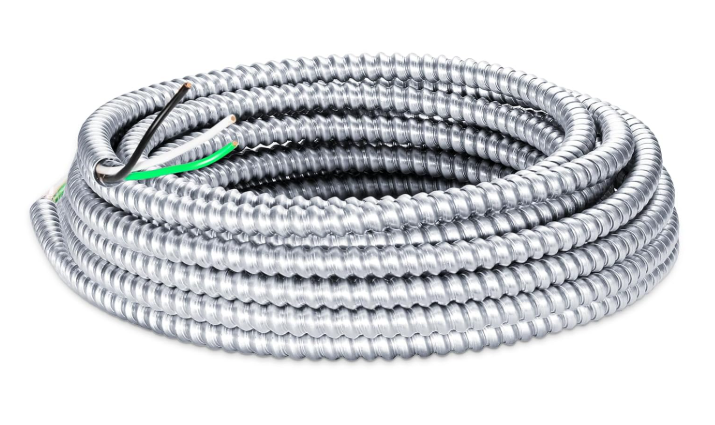
Wiring With MC Cable
Metal-Clad (MC) cable is a cable assembly recognized by the National Electrical Code (NEC) for various applications across residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Its design features insulated conductors encased in a metallic sheath, providing enhanced mechanical protection and grounding capabilities. The 2023 NEC outlines specific provisions regarding the permitted and prohibited uses of MC cable, as well as the different types available and their respective applications.
Permitted Uses of MC Cable
According to 2023 NEC Article 330.10(A), MC cable is permitted in the following scenarios:
- General Use: Metal-Clad cable can be installed in commercial, industrial, and residential buildings, offering flexibility across various construction types.
- Environmental Air Plenums: It is suitable for installation in environmental air spaces, provided it meets the requirements of NEC Article 300.22.
- Hazardous Locations: When listed and marked for such use, MC cable is permissible in hazardous (classified) locations as defined in NEC Article 500.
- Health Care Facilities: Metal-Clad cable is approved for use in health care settings, adhering to the stipulations of NEC Article 517.
- Places of Assembly and Theaters: It is allowed in places of assembly (NEC Article 518) and theaters (NEC Article 520), accommodating the specific needs of these environments.
- Under Raised Floors: Metal-Clad cable can be installed under raised floors for information technology equipment as per NEC Article 645.
- Power and Lighting Control: It is applicable for power, lighting, and control circuits, including dimming systems, in accordance with NEC Article 725.

Prohibited Uses of MC Cable
Per 2023 NEC Article 330.12, the use of MC is restricted in the following conditions:
- Where Subject to Physical Damage: MC cable should not be installed in areas where it is susceptible to physical harm unless adequately protected.
- Corrosive Environments: In environments exposed to destructive corrosive conditions, MC is prohibited unless the metallic sheath or armor is resistant to such conditions or is protected by materials that are.
- Direct Burial: MC is not suitable for direct burial in the earth or embedding in concrete unless it is a specific type of MC (such as PVC-jacketed MC cable) identified for direct burial applications.
Types of MC Cable and Their Applications
MC cables are manufactured in various types, each designed for specific applications:
- Standard MC Cable: Features interlocking metal tape armor, commonly used in general wiring applications within commercial and industrial buildings. It typically includes THHN/THWN conductors and a bare aluminum grounding wire.
- MC-HL Cable: Designed for hazardous locations, this type has a gas/vapor-tight continuous corrugated metallic sheath, an overall jacket of suitable polymeric material, and a separate grounding conductor.
- Jacketed MC Cable: Equipped with an additional nonmetallic (PVC) jacket over the metallic sheath, making it suitable for wet locations.
- Aluminum Interlocked Armor (AIA) MC Cable: Utilizes a strip of aluminum wrapped in a spiral around the cable, offering flexibility and mechanical protection, commonly used in industrial settings.
- Continuously Corrugated Welded (CCW) MC Cable: Features a smooth, continuous metal sheath, providing superior protection against moisture and corrosive elements, ideal for harsh environments.
Installation Considerations
When installing Metal-Clad cable, adherence to NEC requirements is crucial:
- Support and Securing: MC must be supported and secured at intervals not exceeding 6 feet and within 12 inches of each termination point, as specified in Article 330.30.
- Bending Radius: According to Article 330.24(B) for interlocked-type armor or corrugated sheath MC the radius of the inner edge of any bend should not be less than seven times the external diameter of the cable, ensuring no damage occurs during installation. (For smooth sheath MC of various diameters there are different diameters, check 330.24(A) for specifics when using smooth sheath MC)
- Use of Anti-Short Bushings: While not mandated by the NEC, the use of anti-short bushings is recommended by manufacturers to protect conductors from sharp edges. Armored Cable (Type AC), very similar to MC cable, has a requirement in 320.40 to use anti-short bushings, while MC does not; however, many manufacturers include a package of them with newly purchased rolls of MC as an added convenience.
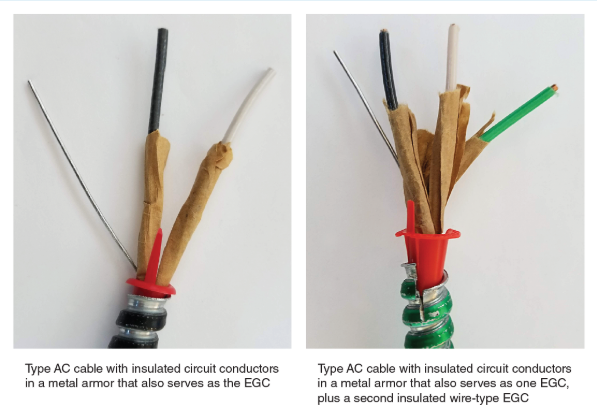
Conclusion
The 2023 National Electrical Code (NEC) provides clear guidelines on the permitted and prohibited uses of MC, ensuring safety and compliance in electrical installations. Understanding the various types of MC cable—such as standard MC, MC-HL, jacketed MC, Aluminum Interlocked Armor (AIA), and Continuously Corrugated Welded (CCW)—and their specific applications is crucial for electricians and engineers. Adhering to NEC requirements, including proper support, securing, and maintaining appropriate bending radii, is essential to maintain the integrity and performance of MC cable installations. By staying informed about code specifications and the characteristics of different Metal-Clad cable types, professionals can ensure safe, efficient, and code-compliant electrical system designs. Want to keep reading? Check out the article “Securing and Supporting NM Cable: A Guide to NEC Compliance” Next!